[fire comment] fire protective clothing, firefighter's "character"
Everyone knows that fire fighters are fighting in the sea of ​​fire, in car accidents, in natural disasters, and on the first front of rescue operations. Every minute and every second has to face unknown and unexpected dangerous situations to protect the lives of firefighters. Security, that is, the protection of disaster-affected people can be rescued at the first time. It is also a valuable professional for the protection of firefighters in this country without dereliction of duty. Therefore, in this issue, Xiao Bian talks with everyone about fire protective clothing. Types of protective clothing Protective clothing belongs to a category of functional clothing and is mainly used to protect firefighters from physical, chemical and biological factors in various work environments. According to statistics, China needs 8 million sets of protective clothing and 10 million sets of special protective clothing every year. Apart from equipment for fire fighters, various workers in the labor protection and hazardous chemicals industries are also demanders of such protective clothing. According to the different fields, protective clothing can be divided into public service, military, medical and health, soil, construction and agriculture, entertainment and other major categories; according to different protective objects, protective clothing can be divided into Two categories: general protective clothing and special protective clothing. Firefighters use special work protective clothing. Special protective clothing is a kind of protective clothing that is worn under special circumstances. Its types include flame-retardant and thermal insulation clothing, cold and warm clothing, anti-static clothing, chemical protective clothing, waterproof clothing, radiation protection suits, and anti-virus suits. Fire and natural disaster protection needs. Protective clothing classification The first element of protective clothing design: safety first The American scholar RFGoldman put forward the "4F" principle in the process of clothing design development: Fashion (Fashionability); Fit (Fit Offset); Feel (Comfort); Function (Functionality). However, for protective clothing, it does not fully apply to the “4F†principle. For firefighters, the first element of fire protective clothing is “safeâ€! The second factor is the comfort of protective clothing. While ensuring the safety of our firefighters, we must not let the protective clothing affect the work efficiency. It is the demand of our firefighters. Different from ordinary clothing design, the design of protective clothing must take into account the use of the environment and the risk of operations, so its number, style, structure and color, etc. must have special considerations. Take firefighters' clothing as an example. Its components include: hoods, helmets, T-shirts, coats, trousers, slings, gloves and boots. In terms of apparel fabrics, it is generally divided into four layers of structure, which are outer and inner shells, vapor barriers, insulation and comfort layers. Kevlar, PBI and other fiber fabrics are used in the outer shell layer, which have non-flammable or flame-retardant, high-temperature resistant, puncture-proof properties; PTFE fiber membranes and other fabrics are used for the vapor barrier layer, which can block the intrusion of the outer layer of high-temperature droplets. Must have breathable comfort; thermal insulation layer uses Nomex fabric to block external heat; comfort layer is the innermost layer, close to the human body, generally use natural cotton or cotton blended fabric to provide comfort. Chemical protective clothing There are many types of fire protective clothing, if all are listed, enough to write a paper. So, let's talk about the common chemical protection suits that fire fighters use. Do you remember the Tianjin bombing in 2015? Many firefighters were killed and injured and everyone doubted the role of protective clothing. In fact, after the firefighters entered the fire scene, the two big explosions equivalent to 24 tons of TNT equivalent were the main cause of firefighters’ deaths and injuries. Under that kind of explosion, advanced protective clothing is just like shredded paper. Tianjin bombing Of course, such extreme cases cannot eliminate the importance of chemical protective clothing for firefighters. Firefighters' chemical protective clothing (CPE) is the protective clothing worn by firefighters when handling chemical accidents. It originates from military nuclear and biochemical protective clothing (NBC). The original intention of the design is to prevent steam and gases including chemical agents and toxic industrial chemicals. , liquids and micro-particles infiltration of the human body. The chemical protective clothing for firefighters is divided into three types according to the types of fabrics: limited use, repeated use, and selective adsorption; according to style, it is divided into body type, conjoined type, and fully enclosed type; seams are divided into sewing seams, overlocks, and ultrasonic heat. Melt, anti-chemical strip seals, strip seals, etc. When dealing with various types of chemical incidents, fire fighters face toxic, hazardous or flammable and explosive materials and chemicals. In many cases, firefighters enter the operating environment with an unknown degree of danger and require the highest level of protection. Many chemicals have a direct corrosive effect on the human body's sucking system and skin, or cause harm to the human body through absorption on the skin, or cause dermatitis, allergies and other illnesses due to exposure to chemicals. Its degree of harm may cause fire fighters to become ill, cripple or even endanger their lives. Therefore, the use of chemical protective clothing for firefighters in the civil fields such as firefighting and emergency rescue has become more and more extensive, and has become a necessary protective equipment for fire fighting teams to carry out firefighting and rescue operations in the environment of chemical dangerous goods. Split chemical protective clothing The main use of chemical protective clothing All types of fire protection suits have strict rules and regulations for use, and chemical protection suits are no exception. Let's learn. First of all, chemical protective clothing wearers must be aware of the scope of use of chemical protective clothing for first- and second-level firefighters before use. If a chemical protective suit is used, it must not be in direct contact with flames and melts; contact with sharp objects must not be avoided. Broken, damaged. Before the use of secondary chemical protective clothing, the clothing must be inspected carefully for damage. If it is damaged, it is strictly prohibited. Second, it must be helped during the process of dressing. In addition, the detachment process must be assisted and monitored by ancillary personnel. The following 7 checks must be performed before use: (1) Whether the gloves and rubber boots are installed correctly; (2) whether it is contaminated inside or outside the garment; (3) Whether there are holes or cracks in the fabrics and connecting parts; (4) Whether the sealing zipper operation is normal and the sliding state is good; (5) Is the overpressure exhaust valve damaged and the diaphragm working properly? (6) Whether the window is damaged or not and whether it is coated with Baoming fluid (the window coated with Baoming fluid should not be fogged); (7) Whether the airtightness of the whole outfit is good or not. Conclusion With the development of science and technology, in addition to protecting the purpose of protective clothing, protective clothing will also develop in a more comfortable, more favorable and ten-human health. How to reduce the load of clothing, adjust the microclimate inside the clothes, carry out antibacterial processing and so on. This means that firefighters' lives can be better protected.
Duplex Stainless Steels Available
Yuhong Group supplies LDX2101, 2205, Ferralium 255, Zeron 100 and LDX2507 in the form of plate, sheet, strip, bar, pipe, tubing, pipe fittings, flanges and weld wire.
Duplex Stainless Steel Overview
Duplex Stainless Steels, also referred to as austenitic-ferritic stainless steels, are a family of grades with about equal proportions of ferrite and austenite. These steels have a duplex microstructure which contributes to their high strength and high resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Due to their high content of chromium, nitrogen and molybdenum, duplex steels offer good resistance to local and uniform corrosion. Duplex stainless steels have good weldability.
Today, modern duplex stainless steels can be divided into three groups:
Of the duplex grades, duplex 2205 is the most widely used. However, the super duplex steels like Zeron® 100 and LDX2507 are excellent for servicing severe corrosive environments, such as offshore and marine applications. Lean duplex 2101 is available as an economic alternative to 300 series stainless steels.
Duplex Steel Seamless Pipe,Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe,Advertising Media Player Box YUHONG GROUP CO.,LIMITED , https://www.jessro-pipefittings.com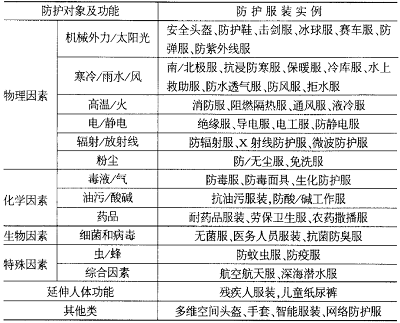



DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL
Lean Duplex such as LDX2101
Standard Duplex such as 2205, the work-horse grade accounting for more than 80% of duplex usage
Super Duplex such as Ferralium 255 and Zeron 100 and LDX2507
What are the Characteristics of Duplex Stainless Steels ?
Very good resistance to uniform corrosion
Very good resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion
High resistance to stress corrosion cracking and corrosion fatigue
High mechanical strength
Good sulfide stress corrosion resistance
Good abrasion and erosion resistance
Good fatigue resistance high energy absorption
Low thermal expansion
Good weldability
In what Applications are Duplex Stainless Steels® used ?
Oil and gas equipment
Offshore technology
Seawater desalination plants
Chemical industry, especially when handling chlorides
Flue-gas cleaning
Desalination plants and seawater systems
Pulp and paper industry
Cargo tanks and pipe systems in chemical tankers
Firewalls and blast walls on offshore platforms
Bridges
Storage tanks
Pressure vessels, reactor tanks, and heat exchangers
Rotors, impellers and shafts