Effective Control of Carburizing and Quenching Deformation of Large Diameter Heavy Duty Gears
Hex Allen Key Set,Hex Key Wrench Set,Flat End Hex Key Set,Craftsman Hex Key Set henan horn tools co.,ltd. , https://www.hornhandtools.com
The gears are subjected to loads such as bending and impact during the transmission process. The quality and performance of gear products, in addition to relying on reasonable and advanced design methods, is mainly determined by the level of gear manufacturing.
According to the different working conditions of the gear, the following basic requirements should generally be met:
(1) The tooth surface layer should have sufficient hardness and wear resistance.
(2) For gears subjected to alternating loads and impact loads, the base should have sufficient flexural strength and toughness.
(3) Good processability, easy cutting and good heat treatment performance.
According to the actual use analysis, high-speed and heavy-duty gears have become the key components of the complete equipment in the automobile and locomotive industry. Most of them use hard-toothed gears. The circumferential speed of the gears can reach up to 150m/s and the transmission power can reach up to 40 000kW. Gear accuracy grades are 5 to 6 and up to 4 grades. In order to achieve the improvement of the localization manufacturing level of these high-precision hard-toothed gears, through the research and manufacturing technology, we have the ability to design and manufacture high-speed gears with a maximum power of 44 000 kW and a high peripheral speed of 156 m/s. Gear manufacturing precision is 4 to 5; heavy-duty gears have a maximum power of 6000 kW, a maximum transmission torque of 2000 kN·m, a peripheral speed of 30 to 50 m/s, and a gear accuracy of 5 to 6.
The high-speed and heavy-load of high-power gears, especially the mass production of carburizing and quenching of large-diameter spoke structures, puts higher requirements on manufacturing precision. Generally, the deformation is controlled, and a quenching press, hot oil quenching or isothermal quenching is often used. However, the configuration of the quenching press requires a certain equipment cost and equipment manufacturing cycle, and the versatility is limited due to structural constraints, and it is difficult to apply to products of various sizes and structures; hot oil quenching or isothermal quenching also has certain equipment. Requirements and corresponding process operations.
Our company's heat treatment workshop, due to a wide variety of products and processes (some Dongfeng 11, Dongfeng 8 locomotives, three types of larger gears, see the attached table, the material is 20CrMnTi), only equipped with the simple equipment required for conventional heat treatment operations ( Heating the furnace body and cooling tank at room temperature). 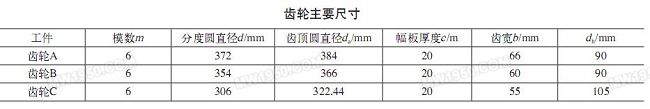
Second, the process and deformation mechanism analysis
The original carburizing and quenching process of the workpiece is: carburizing 930 ° C × (8 ~ 9) h, tempering (600 ~ 650) ° C × 2.5h, quenching 830 ° C × (1.5 ~ 2) h, tempering 180 ° C × 2h. Using a special spreader, the workpiece is laid flat, and each heating process is carried out in a well type carburizing furnace. For a long time, due to the large deformation of the carburizing and quenching of the workpiece, the deformation of the common normal line is 0.40 mm, and the scrap rate is as high as about 10%.
The main reasons for the deformation of the workpiece are:
(1) Thermoplastic deformation is caused by creep at the time of heating at a high temperature.
(2) Phase change process stress During the cooling process, the tissue stress and thermal stress superimpose the dominant stress of the deformation.
(3) Additional stress The stress caused by the difference in composition and texture of the surface layer of the workpiece and the core.
Third, process improvement
Forging blank normalizing
This process is added after the workpiece is roughed. This preliminary heat treatment can obtain ferrite and pearlite structure of uniform equiaxed grains, and promote uniformity of microstructure in different parts of the same batch. This not only ensures that the workpiece has good cutting performance, but more importantly, it reduces the irregular deformation easily caused by carburizing and quenching due to the reduction of the tissue stress and the additional stress which are easily generated in the subsequent heat treatment process.
2. Furnace method
Since the ratio of the temperature to the melting point of the material in each heat treatment process of the workpiece is greater than 0.5, the deformation of the workpiece caused by creep cannot be ignored. This deformation is characterized in that the periphery of the workpiece hangs relative to the central portion during heating, and the strain-time relationship is shown in the drawing. 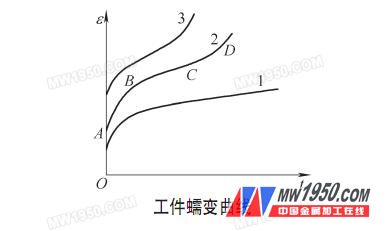
Curve 2 in the figure is a typical creep curve, OA is the elastic deformation of the loading moment, AB is the deceleration creep, BC is the constant velocity creep, CD is the accelerated creep, and the end is the fracture; curve 1 shows the low temperature stress The lower deceleration and the constant speed creep phase are extended; the curve 3 shows the shortening and disappearing of the constant velocity phase under high temperature and high stress.
Creep causes the workpiece to be shortened in the diameter direction, the tooth surface is tapered, and the local common normal line becomes smaller. If the same direction creep occurs after several heatings, the degree of deformation is greater; if the workpiece is quenched after creeping, The creep variable is superimposed on the amount of deformation. When the disc-shaped workpiece is quenched, the plane has a convex or concave deformation tendency due to different dominant stresses, so it has a certain "guide" effect on the quenching deformation, and the convex (concave) deformation in some directions is more severe.
Because the workpiece obeys the creep law in the heating process of carburizing→normalizing→quenching, the temperature and time of the three are decreasing. Therefore, the curve characteristics of different temperatures and times can be compared with the drawing, that is, a part of constant velocity creep can be generated in the carburizing stage, and the ε cumulative value is maximum; normalizing and quenching are corresponding to the deceleration phase, and the ε cumulative value is smaller than the carburizing stage. And ε's value-added speed is higher. It can be seen from the above that although the three-stage creep variable tends to decrease, the reverse creep of the quenching and normalizing processes can largely offset the forward creep of the carburizing process.
According to the above analysis, the placement of the workpiece in the furnace has a great relationship with the deformation. Therefore, in order to ensure the placement position of the workpiece, we adopt the following method: the steel stamp on the same side of the workpiece is marked, and the stamped surface is front, no The stamped surface is the reverse side. When carburizing, the workpiece is placed face up, and the subsequent normalizing and quenching processes are reversed.
3. Normalizing after carburizing
In addition to the creep described above, normalizing also eliminates the reticulated carbides in the surface layer and allows the carbon to continue to diffuse, thereby making the carbon concentration curve of the carburized layer more gradual. This not only effectively increases the strength of the workpiece, but also reduces the additional stress and reduces the time-to-time transition of the martensite to the core, so that the volumetric effects of the microstructure stress and the phase transition of the high and low carbon martensite are The reduction is beneficial to reduce the amount of deformation.
4. Process parameters
Under the premise of not affecting the carburizing effect, the carburizing temperature is reduced from 930 ° C to 920 ° C to reduce the forward creep; under the condition of sufficient phase change, the quenching temperature is reduced from 830 ° C to 820 ° C, and Static oil quenching is used to reduce the quenching intensity and further control the quenching deformation.
It is worth mentioning that domestic and foreign counterparts generally rely on quenching presses and hot oil quenching to solve the problem of deformation of gear carburizing and quenching. However, there is no equipment for controlling deformation in our workshop until now, and the quenching medium is used at ambient temperature. Mixed oil of motor oil and diesel (no additional temperature control during quenching). Sometimes the carburizing process is done in equipment that lacks carbon potential control when equipment conditions do not allow it. However, the practice shows that: under the condition that the structure of the workpiece and the reserved grinding amount are reasonable, the above process can still effectively control the dimensional stability. The above analysis can also explain this phenomenon: Since the workpiece placement direction is random in each heating stage in the past, the reject rate of the oversized size is generally kept within a certain ratio (ie, appears with a certain probability).
Fourth, the conclusion
Through the above analysis and test, we have adopted the following technological measures: gear forging blank normalizing (940 ~ 950 ° C × 2.5h) → workpiece is placed in the carburizing (920 ° C × 8 ~ 9h) → reverse placement Fire (880 ° C × 1.5 ~ 2h) → static oil quenching (820 ° C × 1.5h) → tempering (180 ° C × 2h).
Practice has proved that the process can effectively control the deformation of the workpiece under simple equipment and simple operating conditions. Taking the gear A as an example, the general public line deformation amount is ≤0.01 mm, which almost achieves the effect of using a quenching press. From the current three kinds of gears and the generalized statistics of various gears, the scrap rate caused by dimensional deformation has dropped from the original 10% to the current 1%, which effectively improves the production precision of the product.