Leading progress in luminescence of cationic lead halide materials at Tongji University
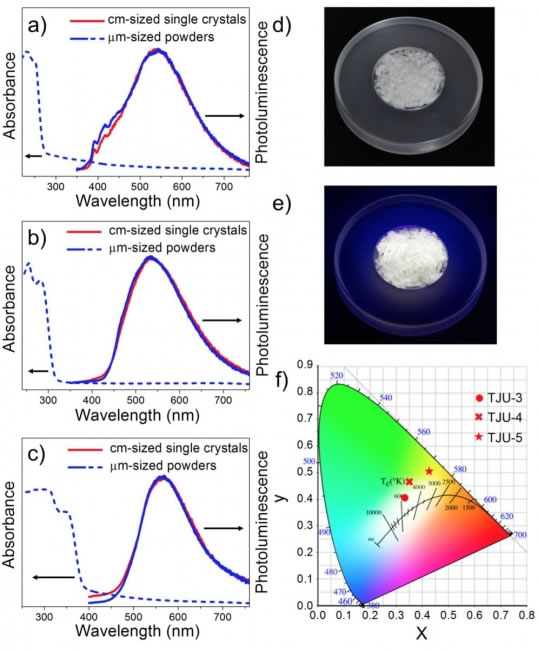
In recent years, a large amount of research on materials and devices for light emitting diodes (LEDs) has made it possible to replace traditional light sources in the field of solid-state white light lighting, and to significantly reduce global lighting energy consumption. One of the key researches in the field of white LEDs today is the development of one-component phosphors with white light emission properties. Only a few of the (110)-plane based lead 2D perovskite structures exhibit unique intrinsic broad-spectrum white-light emission properties and can modulate the luminescent properties of the material through macroscopic crystal structure design. These properties are different from those of conventional nanocrystals. Surface defect mechanism of the material. However, at present, such lead halide perovskite materials have low luminescent quantum yield and poor stability, which greatly limits the practical application of such materials. Faculty of Chemistry and Engineering, Faculty of Chemical Engineering and Engineering, Faculty of Science and Engineering, Faculty of Science and Technology of our school, is devoted to the research of the modification of metal organic frameworks and heterogeneous catalysis and is actively researching the above issues. Recently, the research group used an anion structure directing agent as a template to synthesize a novel type of cationic inorganic lead halide two-dimensional layered lattice material with a structure that exhibits broad spectral emission with large Stokes shift and almost covers The total visible light range, the highest absolute quantum yield of fluorescence is about 11.8%. The metal center coordination environment of these two-dimensional crystal faces of the corrugated cationic lead halide is distorted, resulting in electron-phonon coupling in the distorted crystal lattice, and a large amount of self-trapping ions are generated. The luminescence mechanism studies have shown that the stretching vibration of the Pb-Cl bond in the two-dimensional crystal plane at room temperature overcomes the barrier for electrons to change from the free state to the self-depressed state. More importantly, this type of cationic two-dimensional inorganic lead halide material exhibits excellent chemical stability and photothermal stability. After irradiation with an ultraviolet lamp (4 W, 365 nm) for 30 days at room temperature, the luminous intensity is almost constant. Therefore, this type of material preliminarily solves the disadvantages of lead halide perovskite materials that are sensitive in the air environment, and can further improve their luminescence properties through crystal structure regulation, and has broad application prospects. A few days ago, related research results were published in the international authoritative chemical journal Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., entitled "Intrinsic Broadband White-Light Emission from Ultrastable, Cationic Lead Halide Layered Materials". (Thesis link: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2017, 56, 14411-14416), the research group was the only person who completed the study, Prof. Fei Hanhan was the independent correspondent, and Zhuang Zewen, a subject undergraduate, and Peng Chengdong, a doctoral student, were the co-first authors. Prof. Fei Hanhan joined the Department of Chemistry (now the School of Chemical Science and Engineering) and the Institute of Advanced Studies of Tongji University as a distinguished research fellow in 2015. He was selected as a national youth thousands plan in 2016 and was appointed as a distinguished professor at Tongji University. The above research work was supported by funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51772217), the Youth Fund Project (21501136) and the start-up funding for thousands of young people. Solar Lights,Outdoor Solar Light Strip,Strips Solar Light,Led Solar Light Shenzhen Huangtai Photoelectric Co.,Ltd. , https://www.huangtailightstrip.com