1. Properties of matrix resin
Studies have shown that increasing the toughness of the matrix resin can help to improve the toughening effect of the toughened plastic , and the toughness of the matrix resin can be achieved by:
a. increasing the molecular weight of the matrix resin to make the molecular weight distribution narrow;
b. Improve toughness by controlling crystallization and crystallinity, crystal size and crystal form. For example, the addition of a nucleating agent to the PP increases the crystallization rate and refines the grains, thereby increasing the fracture toughness.
2. Characteristics and dosage of toughening agent
A. Effect of the particle size of the toughener dispersed phase - For elastomer toughened plastics, the properties of the matrix resin are different, and the optimum values ​​of the dispersed phase of the elastomer are also different. For example, the optimum particle size of rubber in HIPS is 0.8-1.3 μm, the optimum particle size of ABS is about 0.3 μm, and the optimum particle size of PVC-modified ABS is about 0.1 μm.
B. Effect of the amount of toughening agent - there is an optimum value for the amount of toughening agent added, which is related to the particle spacing parameter;
C. Effect of the glass transition temperature of the toughening agent - the lower the glass transition temperature of the general elastomer, the better the toughening effect;
D. Effect of interfacial strength between toughener and matrix resin - the effect of interfacial bond strength on toughening effect varies from system to system;
E. Effect of elastomer toughener structure - related to elastomer type, degree of crosslinking, etc.
3. Binding between two phases
The two phases have a good bonding force, which can make the effective transmission between the phases when the stress occurs, and consume more energy. The overall performance of the plastic on the macro is better, especially the impact strength is most remarkable. Usually, this binding force can be understood as the interaction force between two phases. Graft copolymerization and block copolymerization are typical methods for increasing the binding force of two phases. The difference is that they form chemical bonds by chemical synthesis, such as Branch copolymer HIPS, ABS, block copolymer SBS, polyurethane.
For toughening agents toughening plastics, it is a method of physical blending, but the principle is the same. The ideal blending system should be that the two components are partially compatible and each phase is formed, and an interfacial layer exists between the phases. In the interfacial layer, the molecular chains of the two polymers interdiffuse each other, and there is a significant concentration gradient. The compatibility between the components makes them have a good bonding force, which in turn enhances the diffusion and diffuses the interface and increases the thickness of the interface layer. And this, that is, plastic toughening is also the key technology for the preparation of polymer alloys - polymer compatible technology!
Line Construction Hardware
Poleline Construction Hardwares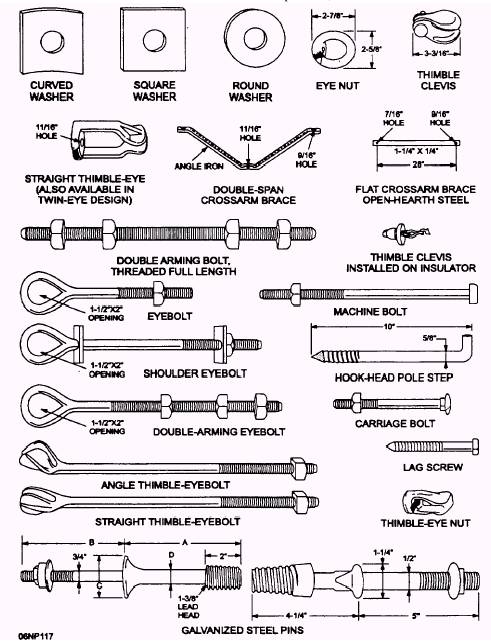
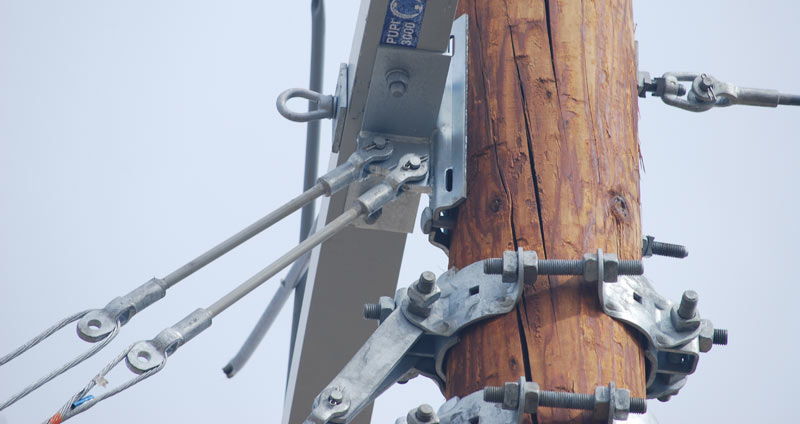
Poleline construction hardware refers to the various components and equipment used in the construction and maintenance of power transmission and distribution lines. These hardware items are designed to support and secure the conductors, insulators, and other components of the poleline system. Some common examples of poleline construction hardware include:
Pole Line Fittings: These are various fittings and attachments that are used to connect conductors to the poles, insulators, and other components. Examples include pole brackets, crossarms, guy wire clamps, and pole bands.
Insulators: Insulators are used to support and isolate electric conductors from the pole or tower structure. They prevent the flow of electric current from the conductor to the ground. Insulators can be made of various materials such as glass, porcelain, or composite materials.
Anchoring and Guying Systems: These systems are used to provide stability and support to the poles or towers. They include guy wires, anchors, deadends, and turnbuckles.
Yokelink supply a full line of Poleline Hardware, we offer from the top of the pole to underground. Here are some of the pole line accessories that you are likely to use for your project

Yokelink Flat Crossarm Brace used to support wood cross arms carrying tangent loads. Round corners on the brace ends prevent damage and reduce the possibility of injury. Hot dip galvanized meet ASTM A153 specification.
Yokelink Alley Arm Brace used for side-arm construction, mounted to one side of the pole, mount at a 45 degree angle and come complete with solidly riveted lineman step. Hot dip galvanized meet ASTM A153 specification.
Yokelink Insulator Brackets are used to mount post type insulators from 15kv to 34.5kv on the side of the pole. Hot dip galvanized meet ASTM A153 specification.
Yokelink Cutout and Arrester Brackets are used for strength and mounting a variety of electrical equipment including arresters, cutouts, combination units and terminations. All components are Hot dip galvanized to meet ASTM A153 specification.
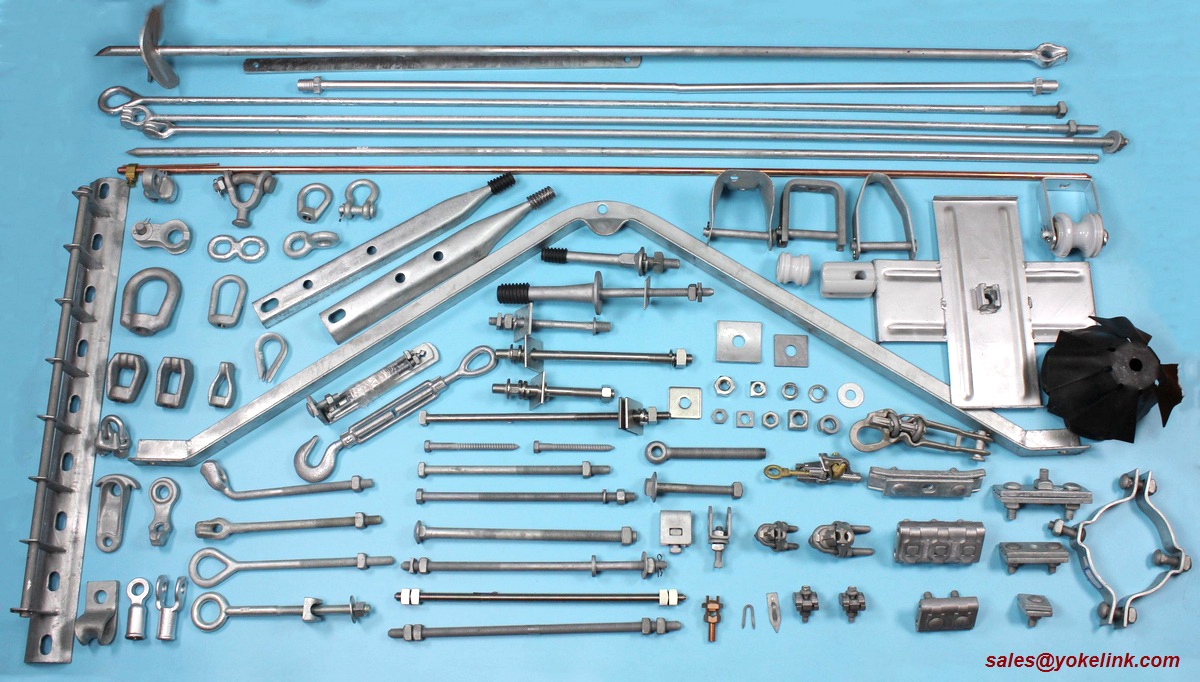
Clevis, Bracket,Transformer, Mounting, Brace, Crossarm, Cutout, Alley, Cross arm, Pole Band
Ningbo Yokelink Machinery Co.,Limited , https://www.yokelink.com


